Southern Hemisphere
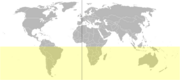
The Southern Hemisphere[1] is the half of a planet that is south of the equator—the word hemisphere (from the Greek word σφαιρα (sphere) +ημι(half)) literally means 'half ball'. It is also that half of the celestial sphere south of the celestial equator.
Earth's southern hemisphere contains all or parts of four continents (Antarctica, Australia, most parts of South America and southern half of Africa), four oceans (South Atlantic, Indian, South Pacific, and Southern) and most of Oceania. Several islands off the Asian continental mainland are also in the Southern Hemisphere. Due to the tilt of Earth's rotation relative to the Sun and the ecliptic plane, summer is December 21 to March 21 and winter is June 21 to September 22. September 22 is the vernal equinox and March 21 is the autumnal equinox.
Contents |
Geography
Climates in the southern hemisphere overall tend to be slightly milder than those in the northern hemisphere except in the Antarctic which is colder than the Arctic. This is because the southern hemisphere has significantly more ocean and less land. Water heats up and cools down more slowly than land. The southern hemisphere is also significantly less polluted than the northern hemisphere because of lower overall population densities (a total of 10 to 12% of the human population), lower levels of industrialisation, and smaller land masses. (Air currents run mostly west–east so pollution does not easily spread north or south.) In the southern hemisphere the sun passes from east to west through the north, although north of the Tropic of Capricorn the mean sun can be directly overhead or due south at midday. The sun rotating through the north causes an apparent right-left trajectory through the sky unlike the left-right motion of the sun when seen from the northern hemisphere as it passes through the southern sky. Sun-cast shadows turn anticlockwise through the day and sundials have the hours increasing in the anticlockwise direction. Hurricanes and tropical storms spin clockwise in the southern hemisphere (as opposed to anticlockwise in the Northern Hemisphere) due to the Coriolis effect.
The southern temperate zone, a subsection of the southern hemisphere, is nearly all oceanic. The only countries that lie entirely within this zone are Uruguay, Lesotho, Swaziland and New Zealand. Countries lying partly in the zone are Chile (most of), Argentina (most of), Paraguay, Brazil, Namibia, Botswana, South Africa (most of), Mozambique, Madagascar and Australia (most of).
The South Pole is oriented towards the galactic centre and this, combined with clearer skies, makes for excellent viewing of the night sky from the southern hemisphere with brighter and more numerous stars.
Forests in the southern hemisphere have special features which set them aside from the northern hemisphere. Both Chile and New Zealand share, for example, unique beech species or Nothofagus. The eucalyptus is native to Australia but has now gone on to be planted in southern Africa and Latin America for pulp production and, increasingly, biofuel uses.
List of continents and countries
Continents

- Antarctica
- Africa (approximately 1/3 of it - from south of Libreville in Gabon in the west to south of Somalia in the east)
- Australia (the entire mainland is in the southern hemisphere, although the very northern part of Raja Ampat Islands in New Guinea are in the northern hemisphere)
- South America (mostly, south of the Amazon River mouth in the east and Quito in the west)
African countries
- Entirely
- Angola
- Botswana
- Burundi
- Comoros
- Lesotho
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mauritius
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Rwanda
- Seychelles
- South Africa
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
- Mostly
- Partly
Asian countries
- Entirely
- Mostly
- Partly
- Southern Malaysia Island
- Malaysia(Not deputed)
Oceania countries
- Entirely
- Mostly
America
- Entirely
- Mostly
- Partly
Other territories
|
|


See also
- Northern Hemisphere
- Seasons
- Solstice
- Equinox
- Tropic of Capricorn
- Crux (or Southern Cross)
References
- ↑ Merriam Webster's Online Dictionary (based on Collegiate vol., 11th ed.) 2006. Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster, Inc.
|
|||||